
In modern-day lab environments, the clinical laboratory microscopes is not just a separation apparatus—it is precision engineering. With simple-to-view digital displays and microprocessor controls, it makes it easy for scientists to quickly adjust variables like acceleration and deceleration rates. Other models come equipped with onboard diagnostics that analyze rotor condition and operating performance. High-end safety features like automatic lid interlocks and imbalance detection offer protection at every cycle. With more rapid and consistent processing needed in industries, clinical laboratory microscopes technology keeps up with stability, precision, and greater throughput capability.
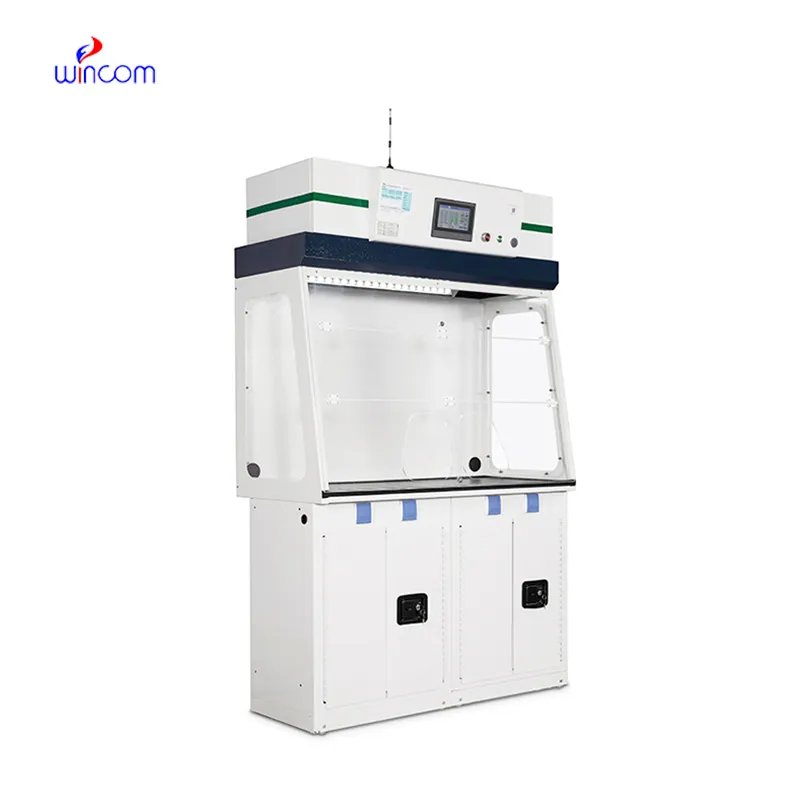

Clinical laboratory environments utilize clinical laboratory microscopes as an important tool for proper diagnosis. Blood banks utilize it to efficiently isolate red cells, plasma, and platelets. Research laboratories employ clinical laboratory microscopes to examine tissue samples for cellular and molecular studies. In the energy industry, it assists in the manufacture of biofuels by isolating the biomass components. Food scientists employ clinical laboratory microscopes to reclaim fats and purify proteins while preparing products. The numerous applications reflect its capacity to enhance data reliability, process control, and yield output in a wide variety of industries and research applications.
Future development of clinical laboratory microscopes will focus on precision control and data integration. Next-generation models will have sophisticated sensors that log every parameter of operation, generating total digital records for traceability. Performance trends will be predicted using machine learning, providing repeatable results. Hybrid clinical laboratory microscopes systems that can perform solid-liquid-gas separations will become a reality. Better safety designs and noiseless operation will make them easier to use. As research demands grow, these intelligent, automated clinical laboratory microscopes will be at the center of labs, enabling faster discovery and industrial productivity globally.
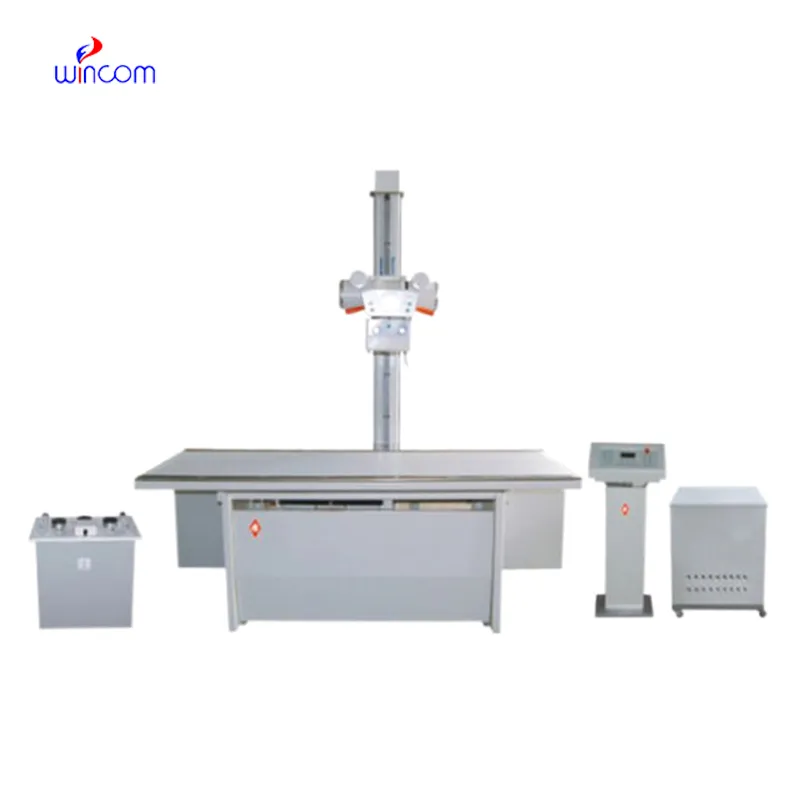

Proper maintenance and care of clinical laboratory microscopes are essential for ensuring accuracy, safety, and long life. Regular checking of rotors for cracks and corrosion eliminates mechanical failure and imbalance. Users must clean the chamber with mild detergent and must not use abrasive chemicals that will damage surfaces. Regular calibration checks must be conducted to ensure speed accuracy. Greasing moving parts according to the manufacturer's recommendation increases motor life. Upon each use, samples need to be withdrawn at once, and open lids to prevent condensation. Periodic maintenance and records provide consistent operation.
Used in many applications, a clinical laboratory microscopes uses rotational motion to facilitate material separation. Working through centrifugal force, it accelerates sedimentation, allowing scientists to sort particles based on density. Used extensively in laboratories, production plants, and environmental testing, the clinical laboratory microscopes simplifies processes that would otherwise be tedious. Flexible, it can be used in anything from clinical diagnostics to food and drinks. With continuing improvement in rotor design and balance technology, clinical laboratory microscopes today offer improved stability, endurance, and accuracy of data than before.
Q: What factors affect the performance of a centrifuge? A: Performance depends on rotor design, speed accuracy, load balance, and regular maintenance of mechanical and electrical parts. Q: How should a centrifuge be cleaned? A: Use a soft cloth and mild detergent to clean the chamber and rotor, avoiding abrasive or corrosive substances that could cause damage. Q: Can a centrifuge be used for temperature-sensitive samples? A: Yes, refrigerated models are designed to maintain stable temperatures, protecting samples from heat generated during rotation. Q: What does RPM mean in centrifuge operation? A: RPM stands for revolutions per minute, indicating how fast the rotor spins—higher RPMs generate stronger centrifugal forces. Q: When should the rotor of a centrifuge be replaced? A: Rotors should be replaced when signs of fatigue, corrosion, or cracking appear, or after reaching the manufacturer’s specified lifespan.
We’ve used this centrifuge for several months now, and it has performed consistently well. The speed control and balance are excellent.
The microscope delivers incredibly sharp images and precise focusing. It’s perfect for both professional lab work and educational use.
To protect the privacy of our buyers, only public service email domains like Gmail, Yahoo, and MSN will be displayed. Additionally, only a limited portion of the inquiry content will be shown.
We’re looking for a reliable centrifuge for clinical testing. Can you share the technical specific...
I’m looking to purchase several microscopes for a research lab. Please let me know the price list ...
E-mail: [email protected]
Tel: +86-731-84176622
+86-731-84136655
Address: Rm.1507,Xinsancheng Plaza. No.58, Renmin Road(E),Changsha,Hunan,China